Stress Testing
July 2024
The Risk Snapshot Series highlights key insights from GARP’s quarterly survey of Financial Risk Managers (FRM®) about critical risk issues global risk managers and their organizations are navigating.
Stress testing is an important forward looking tool for financial risk managers. With proper resourcing, participation, and design, stress testing can help financial institutions improve risk identification, measurement, and mitigation. Many financial institutions are also required to participate in annual regulatory stress tests.
The GARP Benchmarking Initiative (GBI)® invited Financial Risk Manager
(FRM®) Certified Professionals globally to participate in a survey designed
to determine:
- Implementation and maturity of internal stress testing
- Challenges with stress testing
- Effectiveness of internal and regulatory stress testing
Over 1,000 FRM-Certified Professionals responded to the survey, representing a broad range of financial services firms and risk disciplines globally. Roughly 59% of respondents work at large firms (over 1,000 employees) and more than 60% have at least five years of risk management experience. Read on for key insights from the survey results.
Insight #1 – Stress Testing Is a Well Developed Function of Risk Management at Most Firms
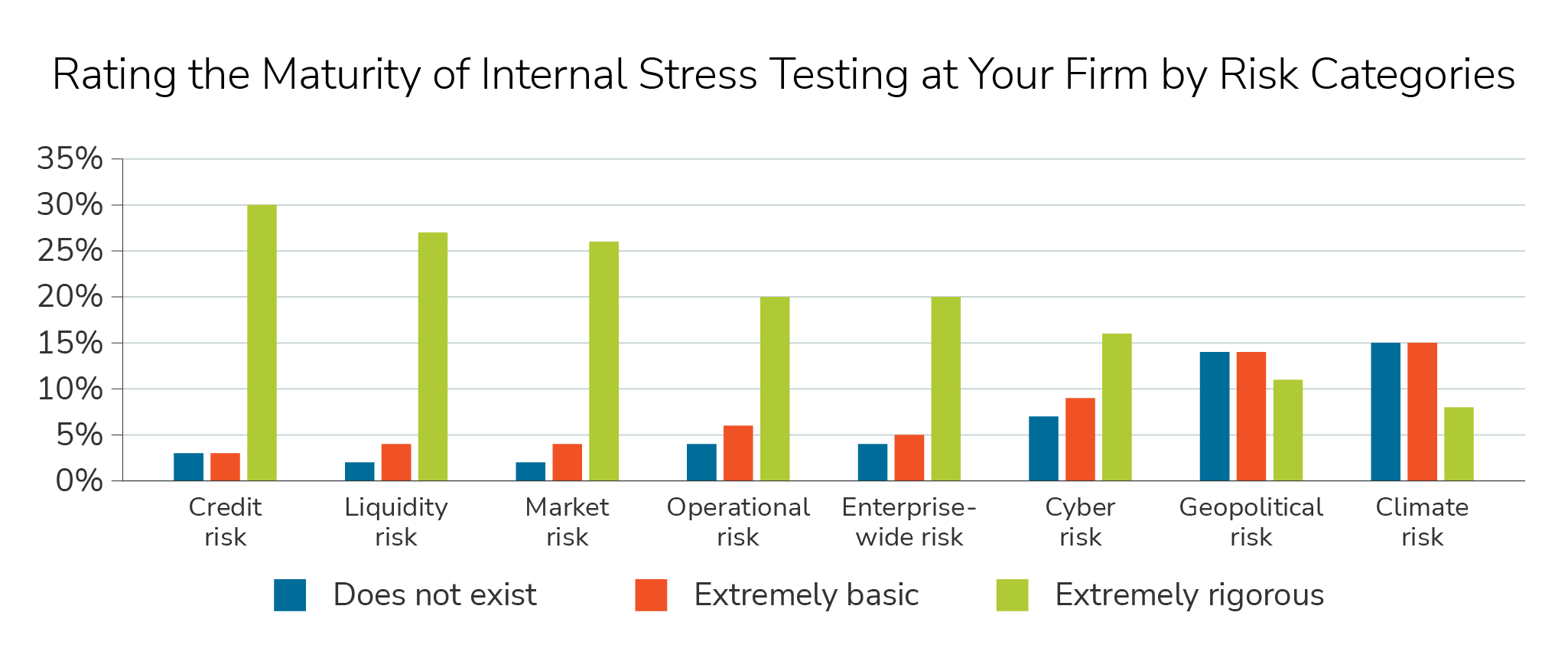
Almost 75% of respondents indicated that their firm’s internal stress testing was at least ‘defined’ and ‘somewhat sophisticated’ with almost 30% saying it was ‘well-defined’ and ‘sophisticated’. Over 25% of respondents felt their internal stress testing frameworks for credit risk, liquidity risk, and market risk were ‘extremely rigorous’. Over 25% of respondents also reported that their internal stress testing frameworks for geopolitical risk and climate risk either ‘does not exist’ or is ‘extremely basic’.
For every category except geopolitical risk, respondents from the Americas were more likely to rate their internal stress testing framework as ‘extremely rigorous’.
Insight #2 – Stress Testing Serves a Wide Range of Objectives
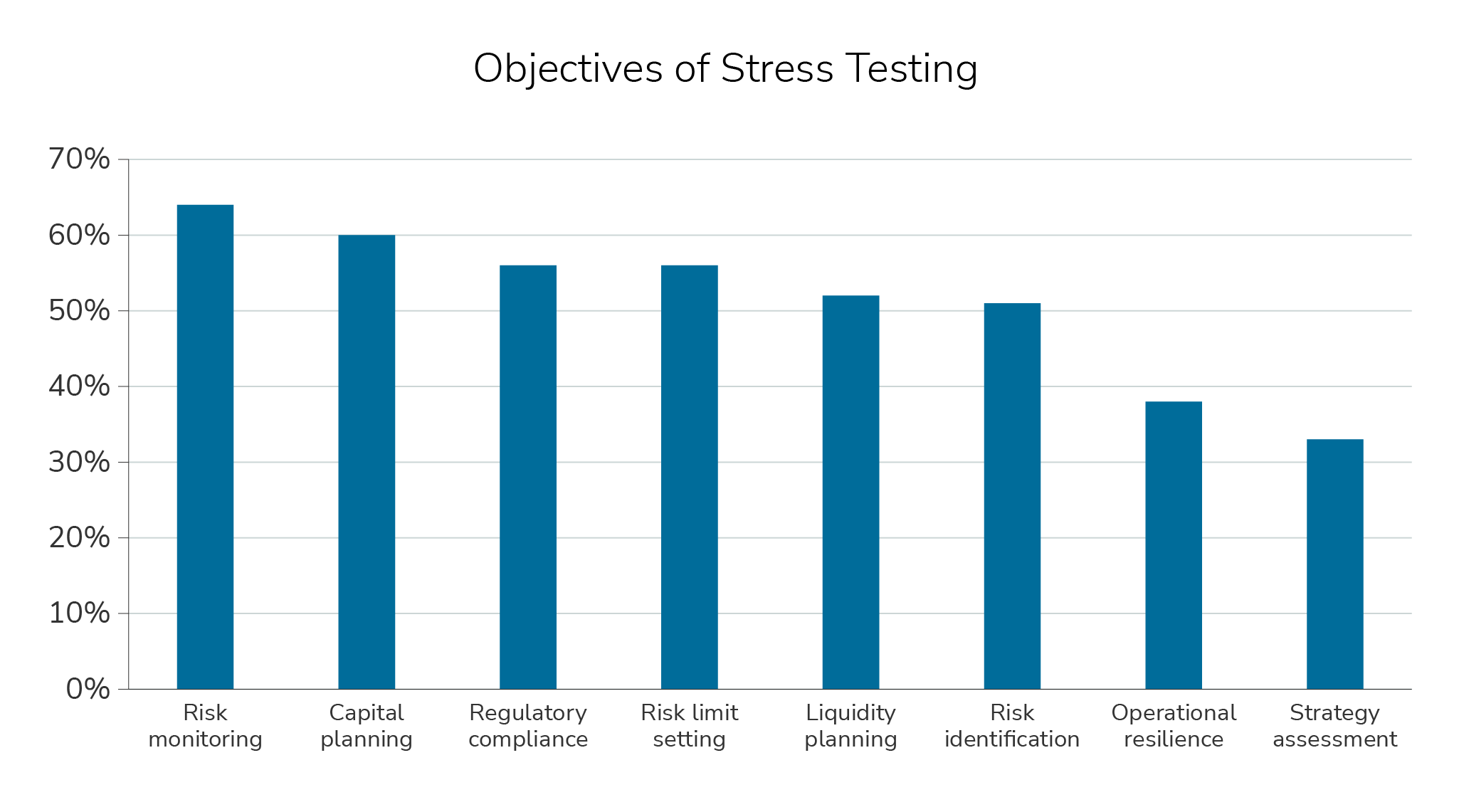
Stress testing serves a wide range of objectives — over 50% of respondents selected risk monitoring, capital planning, regulatory compliance, risk limit setting, liquidity planning, and risk identification as objectives of stress testing within their firm.
Insight #3 - Challenges of Stress Testing
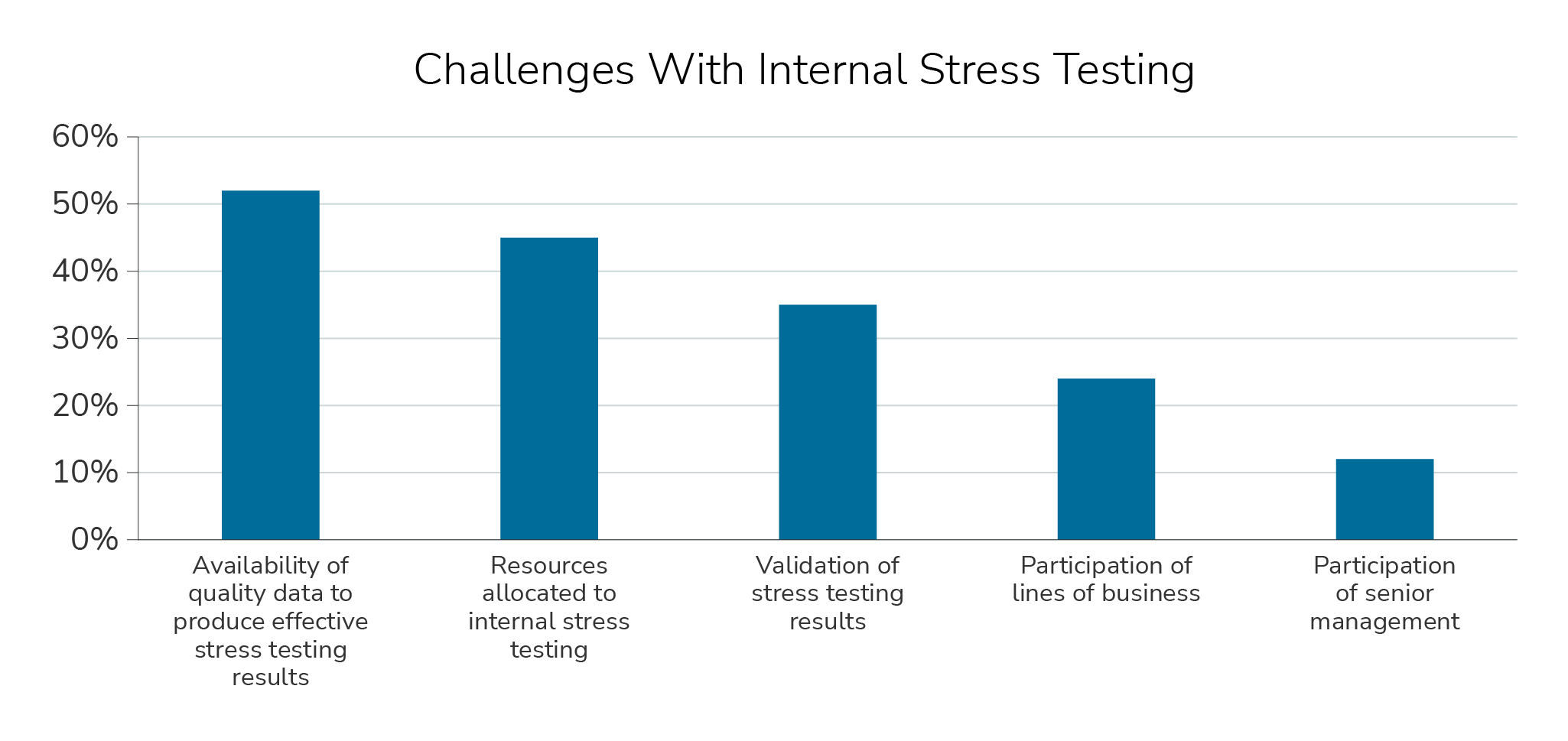
Availability of quality data and sufficient allocation of resources were the two most common challenges with internal stress testing reported by risk managers. Less than 20% of respondents felt that participation of senior management was a problem, which suggests that
there is support from the top for stress testing.
Over 60% of respondents felt that internal stress testing practices have improved over the last two years, with less than 8% reporting that practices have worsened.
Insight #4 –Effectiveness of Stress Testing
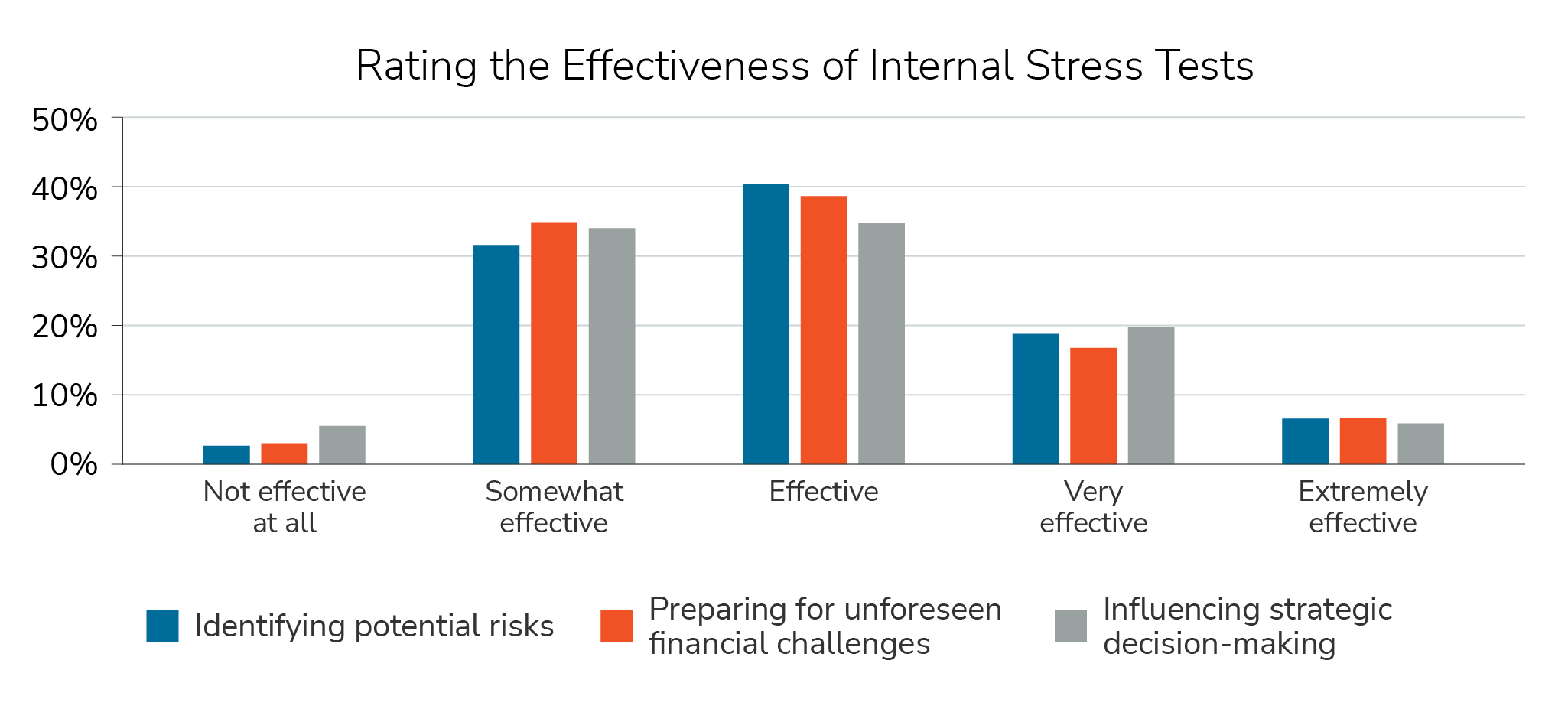
Respondents were consistently moderately satisfied with the effectiveness of internal stress testing with respect to its ability to identify potential risks, prepare for unforeseen financial challenges, and influence strategic decision-making.
Respondents whose firm participates in regulatory stress tests indicated moderate satisfaction with their effectiveness. Seventy percent of these respondents felt that their firm viewed these exercises as integral to capital allocation and risk management.
Insight #5 – Stress Testing and AI/Machine Learning
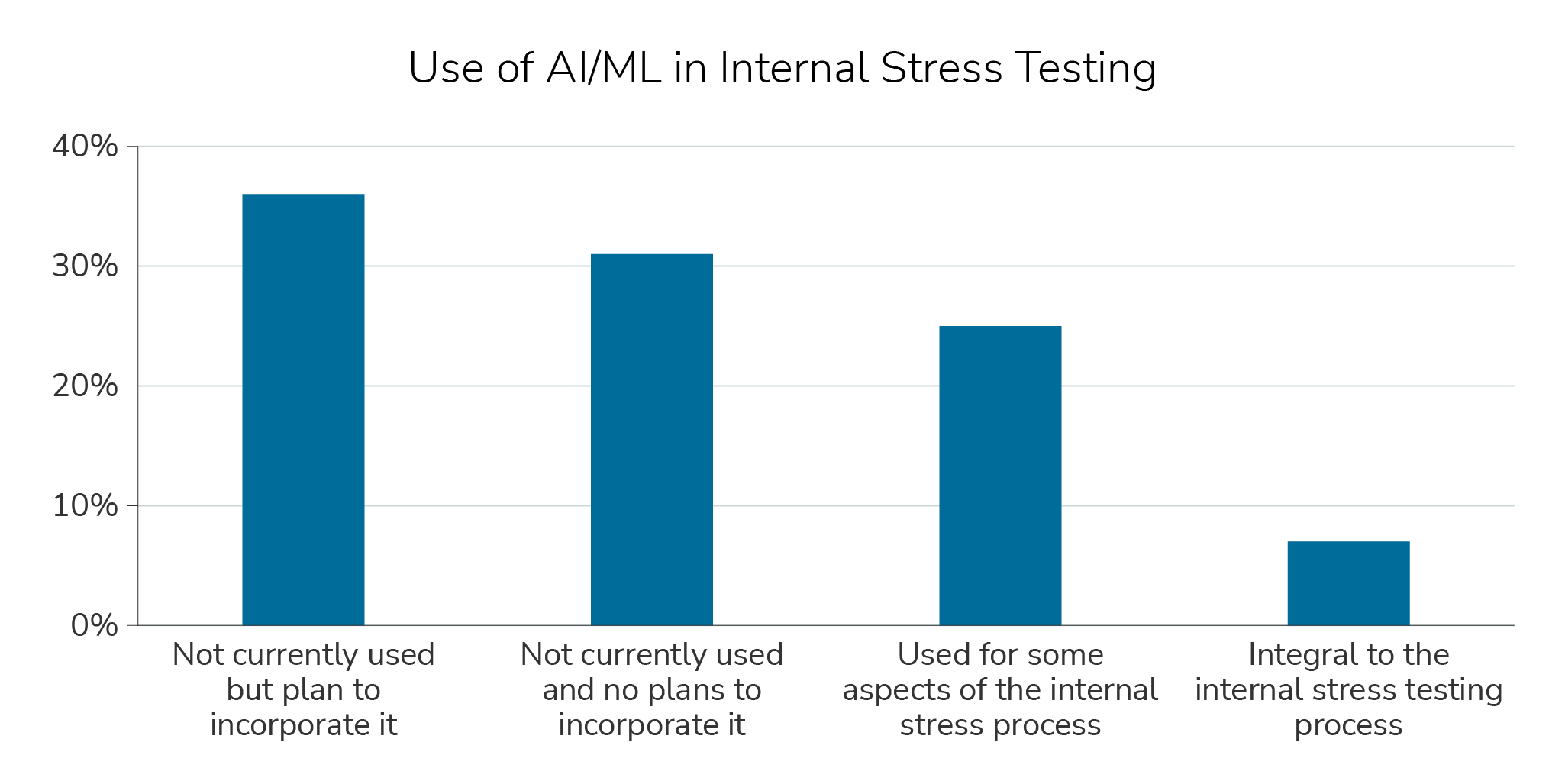
Internal stress testing is just starting to incorporate AI and machine learning (ML) processes. Roughly a third of respondents indicated that AI/ML is used, with 7% reporting that it is integral. Roughly a third also indicated that AI/ML is not currently used in internal stress testing and there are currently no plans to start.
Insight #6 – Internal and Regulatory Stress Testing
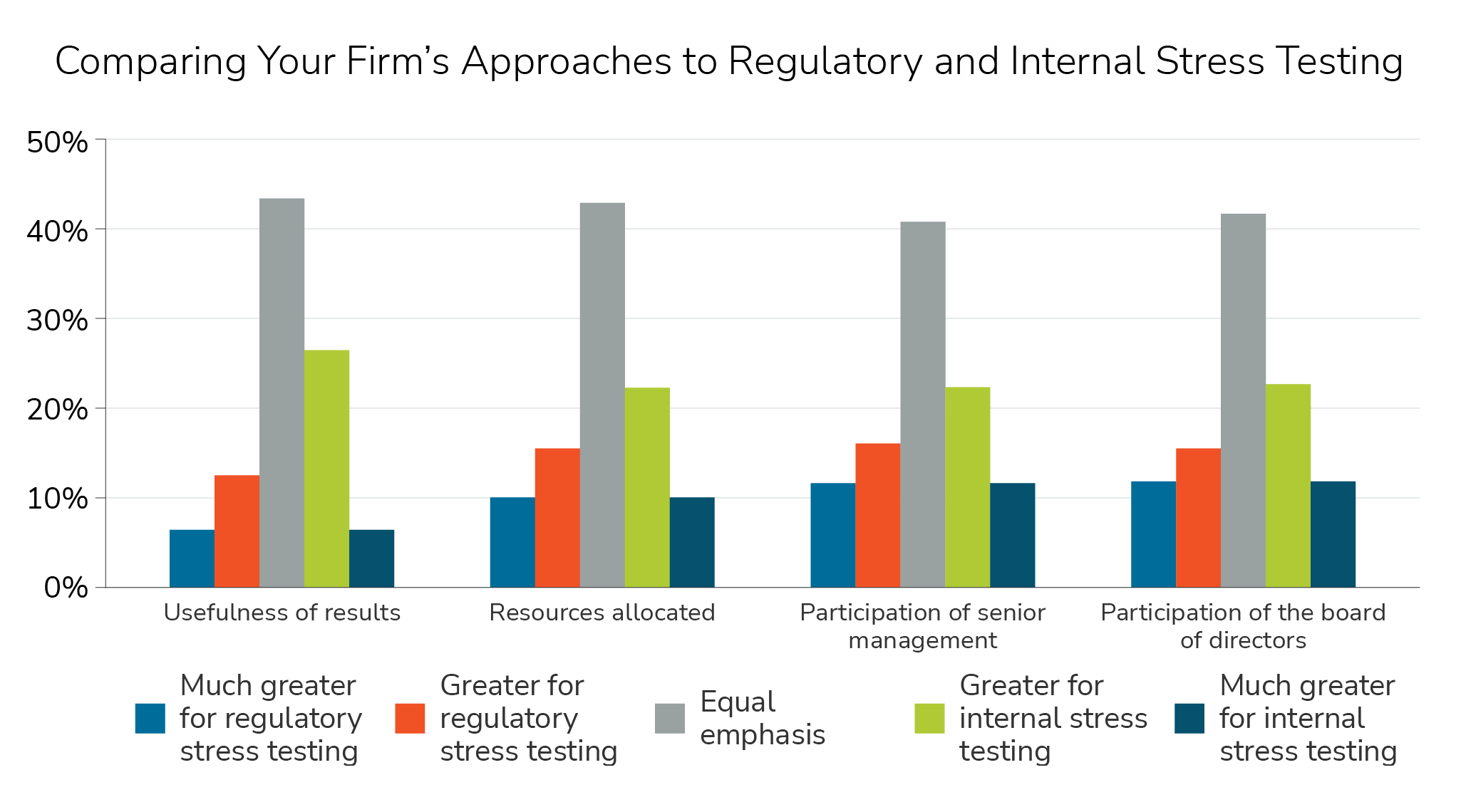
In comparing their firm’s approaches to regulatory and internal stress testing, respondents indicated a fairly balanced view between the two, with most indicating equal emphasis across various dimensions with a slight tilt in favor of internal stress testing.
Survey Demographics
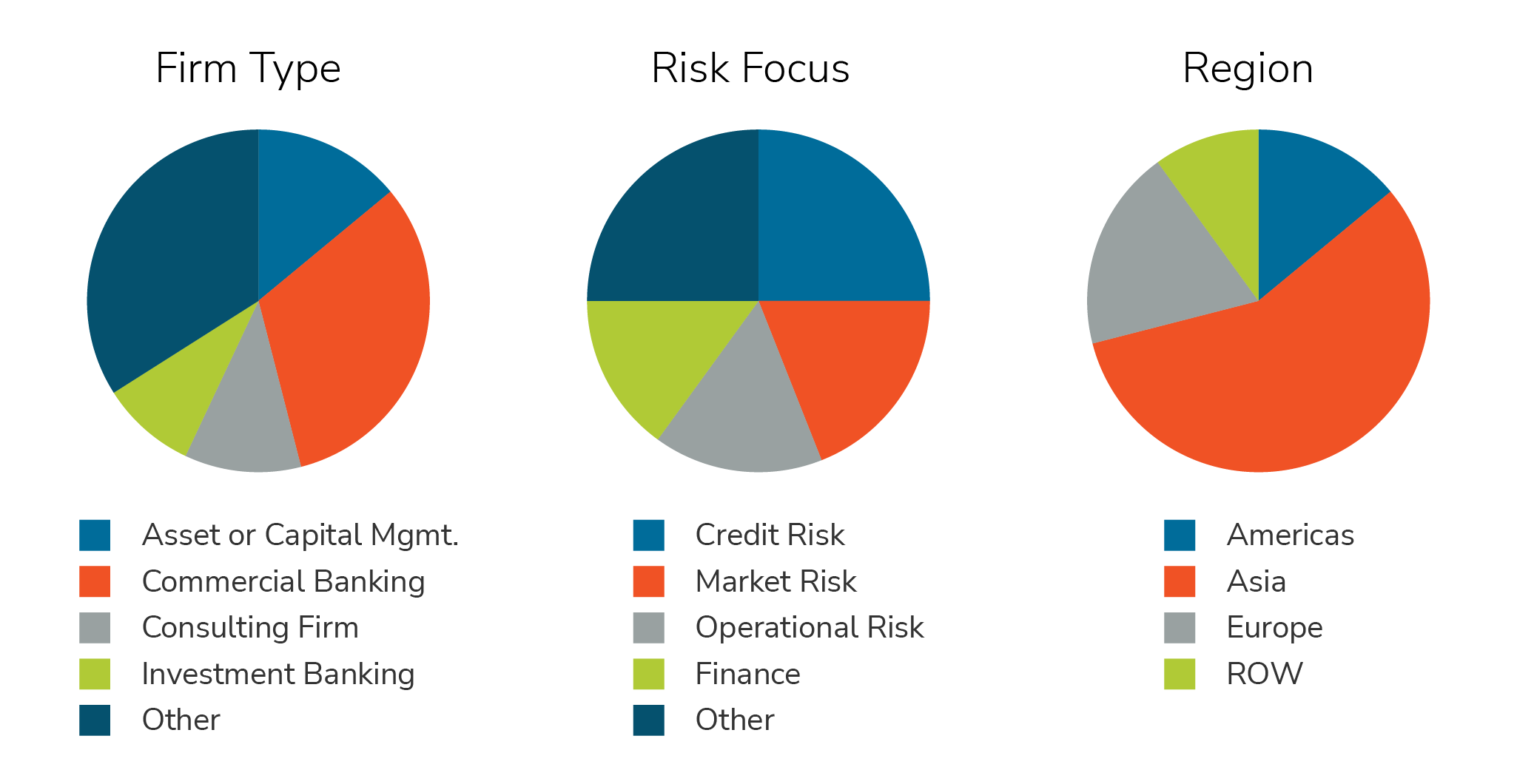
Over 1,000 FRM-Certified Professionals participated in this survey. They represent a broad swath of financial services firms and risk disciplines across the globe as shown in the respondent breakdowns by region, firm type, and primary risk area in the charts below.

Want to read more?
Download the full report now!
